
- #JAVA PLAY SOUND HOW TO#
- #JAVA PLAY SOUND SOFTWARE#
- #JAVA PLAY SOUND FREE#
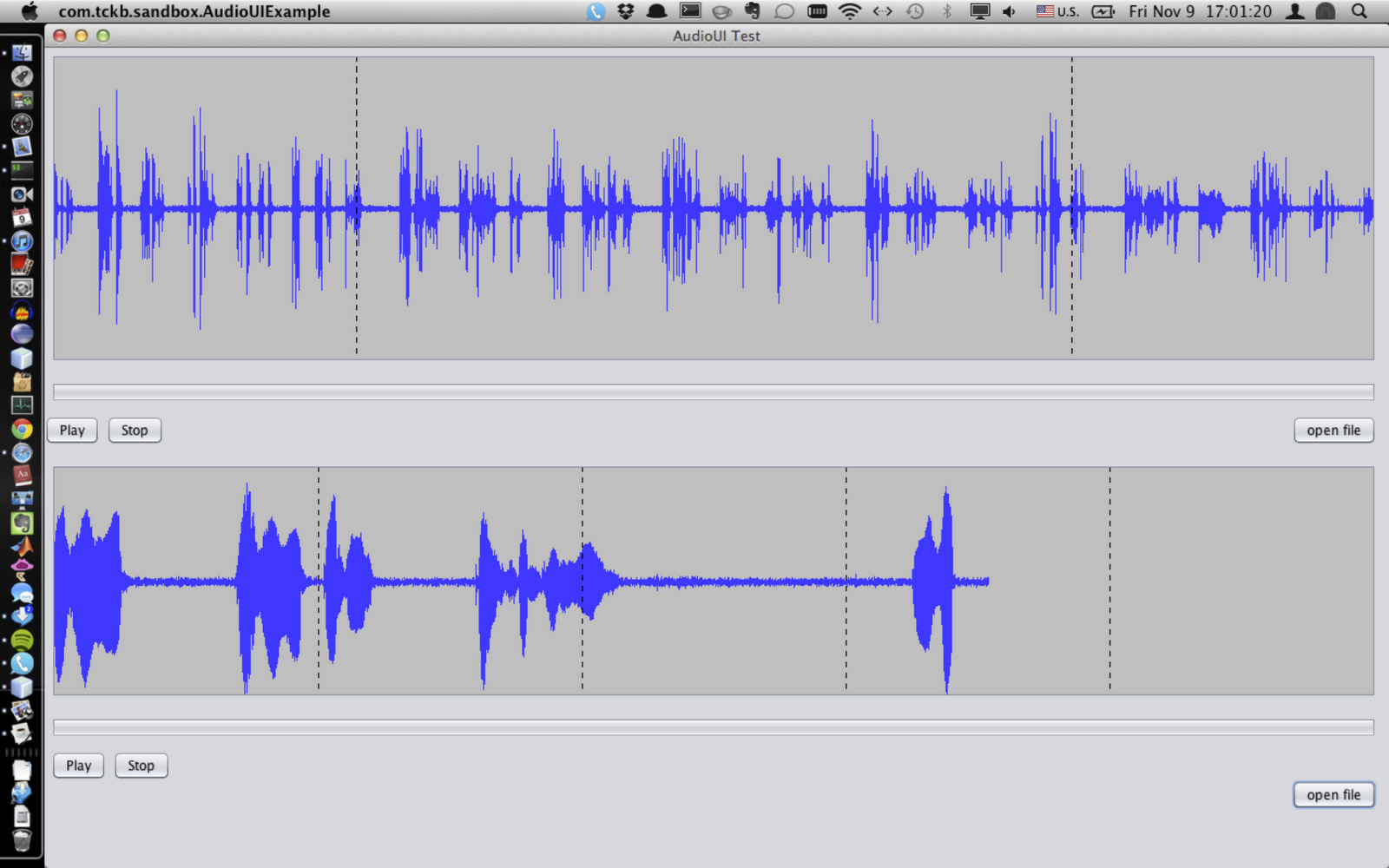
I have to say that the free version of this product is powerful and easy to use. Program 1: Illustrating the implementation of a simple record.To create the sounds I looked up in Google to find a "free audio editor" and I found. Program Change for changing default instrument etcīelow programs illustrate the usage of MIDI in Java:
tMessage(int command, int channel, int data1, int data2) – sets a ShortMessage object that has at most two data bytes (data1 and data2). ShortMessage() – A ShortMessage object with at most two data bytes (Extended from MidiMessage). 
MidiEvent(MidiMessage message, long tick) – A midi event object that contains a time stamped midi message.Track.add(MidiEvent event) – Adds a new event to the track.Track – Class containing midi events arranged chronologically.Sequence.createTrack() – Creates an empty track.Sequence.PPQ – Tempo based timing type, for which the resolution is expressed in pulses (ticks) per quarter note.Sequence – The Sequence class instance holds a data structure representing one or more tracks and timing information.sequencer.isRunning() – Indicates whether the Sequencer is currently running.sequencer.start() – Starts playback of the MIDI data in the currently loaded sequence.
 tTempoInBPM(float bpm) – Sets the playback tempo in beats per minute. tSequence(Sequence sequence) – Sets the current sequence on which the sequencer operates. sequencer.open() – opens the sequencer so it can acquire system resources. MidiSystem.getSequencer() – returns an instance of the sequencer interface which is connected to a synthesizer/receiver. All methods are static and this class can’t be instantiated. MidiSystem: This class provides access to installed MIDI resources like sequencers, synthesizers, I/O ports. Sequence: It is a data structure containing multiple tracks and timing information.The sequencer takes in a sequence and plays it. Track: It is a sequence of Midi events. We can send off a midi event to any of those channels which are later synchronized by the sequencer. Channel: Midi supports upto 16 different channels. It arranges events according to start time, duration and channel to be played on. Sequencer: A sequencer takes in Midi data(via a sequence) and commands different instruments to play the notes.
tTempoInBPM(float bpm) – Sets the playback tempo in beats per minute. tSequence(Sequence sequence) – Sets the current sequence on which the sequencer operates. sequencer.open() – opens the sequencer so it can acquire system resources. MidiSystem.getSequencer() – returns an instance of the sequencer interface which is connected to a synthesizer/receiver. All methods are static and this class can’t be instantiated. MidiSystem: This class provides access to installed MIDI resources like sequencers, synthesizers, I/O ports. Sequence: It is a data structure containing multiple tracks and timing information.The sequencer takes in a sequence and plays it. Track: It is a sequence of Midi events. We can send off a midi event to any of those channels which are later synchronized by the sequencer. Channel: Midi supports upto 16 different channels. It arranges events according to start time, duration and channel to be played on. Sequencer: A sequencer takes in Midi data(via a sequence) and commands different instruments to play the notes. #JAVA PLAY SOUND SOFTWARE#
It can either be a software synthesizer or a real midi compatible instrument.
Synthesizer: This is the device that plays the midi soundtrack. The transmitter objects implement the Transmitter interface, and the receivers implement the Receiver interface.Įach transmitter can be connected to only one receiver at a time, and vice versa Transmitters and Receivers : The way a device sends data is via one or more transmitter objects that it “owns.” Similarly, the way a device receives data is via one or more of its receiver objects. 
It also includes an inner class called MidiDevice.Info that provides textual descriptions of the device, including its name, vendor, and version. MidiDevice Interface : The MidiDevice interface includes an API for opening and closing a device.Java Sound API’s Representation of MIDI Device Split() String method in Java with examples.How Do I Become a Good Java Programmer?.Using predefined class name as Class or Variable name in Java.Monolithic vs Microservices architecture.
#JAVA PLAY SOUND HOW TO#
How to run java class file which is in different directory?. Myth about the file name and class name in Java. Does JVM create object of Main class (the class with main())?. ISRO CS Syllabus for Scientist/Engineer Exam. ISRO CS Original Papers and Official Keys. GATE CS Original Papers and Official Keys.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
